Web Data Service - WDS-Cookbook 1.0.0
Introduction
The huge number of available formats and tools to save and exploit data produces a wide array of solutions. This abundance raises another issue: the level of knowledge and required technologies to exploit data sources using different solutions and orientations. The environments are not seamless. This represents an issue when exploiting data from different providers. The result of this experiment is the Web Data Service, which is designed chiefly as a solution for data exploitation issues.
A Web Data Service (WDS) consists in a Framework aimed at promoting interoperability between systems by supporting the development of Web data services. The Framework uses SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) best practices.
The SOAP technology and the HTTP protocol are used to create the WDS Framework. WDS services can be developed according to a choice of language and infrastructure selection.
The SOAP technology is available on most platforms and programming languages. This feature reduces system coupling and the level of knowledge required for data exploitation. Expertise is maintained in the proper spheres so that a client-system developer no longer has to acquire the expertise of the data source. The client-system merely uses a SOAP client to access data from a WDS service. No specific knowledge of data architecture is needed.
WDS Architecture

Generic Specifications
- Latitude is expressed in fractional degrees ([-90, 90]).
- Longitude is expressed in fractional degrees ([-180, 180]).
- Date format is the ISO-8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss) and the time zone is UTC.
- The unit of measurement used for depth is the meter.
Class Diagram

WDS Interface
This interface provides the necessary functionalities for creating a data access service. The WDS interface is used to implement a WDS Web service.
This method provides the WDS Framework version implemented in the data service.
This method provides the data service name.
This method provides various generic information on the data service.
This method provides the data service status.
latitudeMin: double,
latitudeMax: double,
longitudeMin: double,
longitudeMax: double,
depthMin: double,
depthMax: double,
dateMin: string,
dateMax: string,
start: integer,
sizeMax: integer,
metadata: Bool,
metadataSelection: string,
order: String): ResultSet
This method provides a way to search the data service. Results are ordered by date.
Parameter description:
latitudeMin: minimum latitude
latitudeMax: maximum latitude
longitudeMin: minimum longitude
longitudeMax: maximum longitude
depthMin: minimum depth
depthMax: maximum depth
dateMin: start date
dateMax: end date
start: result start number (>0)
sizeMax: maximum result size (>0)
metadata: include metadata in results
metadataSelection: metadata selection criteria ("" = none)
This parameter provides a way to narrow down the search to
elements meeting certain metadata values. The metadata parameter does not
influence the metadataSelection
parameter.
Syntax: "metadata_1=value::metadata_2=value::metadata_n=value"
Example: "station_name=Rimouski"
Example: "station_name=Rimouski::semaphore=2"
asc: ascending (oldest to most recent)
desc: descending (most recent to oldest)
Datatype ResultSet
This type represents search results.
Datatype BoundarySpatial
This type represents spatial boundaries.
Datatype BoundaryDepth
This type represents depth boundaries in meters.
Datatype BoundaryDate
This type represents time boundaries (ISO-8601).
Datatype Status
This type represents a status.
Datatype Metadata
This type represents a metadata.
Datatype Data
This type represents a data.
List of spatial coordinates representing the data.
line: list of coordinates
polygon: list of coordinates where the first and last have the same value
How to build a Web Data Service (WDS)
Building a WDS is a simple operation. All that is required is to implement the WDS interface (see class diagram) in a given language and make it available on a selected SOAP server. Implementation is regulated by a series of rules that must be followed in order to respect the Framework and to make the service’s behaviour consistent with WDS specification. The generic specifications initially described must always be respected.
Rules
Example: "1.5.4". This information is necessary to know the service’s conformity with the Framework. This version of the cookbook is consistent with version "1.0.0".
Example: a short description along with the contact and URL for more information
- the unit is the meter
- negative values are prohibited
- The ISO-8601 standard is used for presenting dates (YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss). All elements in the format must be present.
- The time zone is UTC.
- The ISO 19115 standard must be used for geospatial type metadata. The standard’s minimum metadata are essential. They are described below:
date: date service was created
language: service language
topic: service subject
name: service name
abstract: brief description of service
reference_date: service time boundaries
- It is recommended that a recognized standard be used for other types of metadata.
- Every parameter of the method is mandatory and must be validated.
- Data exceeding service boundaries (spatial, depth, time) must be rejected.
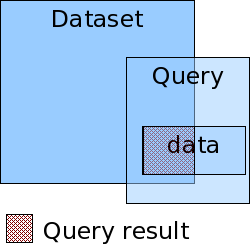
- Data that does not meet metadataSelection parameter requirements must be rejected.
- Data must be sequenced according to date as per the order parameter value.
- The start parameter is applied once the data has been sequenced.
- A maximum number of data for a query must be defined in order to avoid overexploitation of the data source. The sizeMax parameter could be a very large number.
- Metadata must be included (ResultSet, Data) when the metadata parameter requires it.
- Coordinates associated to a data must respect an appropriate structure according to the spatial type of the object.
line: list of coordinates
polygon: list of coordinates where the first and last are identical.
- A table, must, at least be of size 0.
How to exploit a Web Data Service (WDS)
The basis of SOAP based architecture makes its exploitation by a system very simple. All that is needed is to use a SOAP client on a selected platform and language to access the WDS service and interact with the WDS interface methods.
| import sys | |
| from SOAPpy import WSDL | |
| server = WSDL.Proxy(sys.argv[1] + "?wsdl") | #connect |
| bnds = server.getBoundarySpatial() | #call |
| print "lat: (%.2f, %.2f) lon: (%.2f, %.2f)" %\ | #digest |
| (bnds.latitude.min,
bnds.latitude.max, bnds.longitude.min, bnds.longitude.max) |
#results |